Redis Reconnect Strategy in NestJS
Caching data represents a pivotal strategy for bolstering the performance of our NestJS application. It empowers us to retain information from requests directed towards external APIs, particularly when these requests tend to yield identical responses.
Consider the following scenario: our initial request to an external API incurs a response time of 1537 ms (see fig.1). However, as the response content remains consistent, subsequent requests benefit from cached data, slashing the response time to a mere 38 ms (see fig.2).
This article delves into the intricate Redis Reconnect Strategy within NestJS, explaining how such a mechanism optimizes caching procedures and fortifies the efficiency of our application. Join us as we explore the nuances and implementation techniques that underpin this pivotal strategy.


How to Configure Redis in NestJS?
Configuring Redis in NestJS involves importing the CacheModule alongside the redisStore provided by the @nestjs/cache-manager and cache-manager-redis-store NPM packages, respectively.
@Module({
imports: [
CacheModule.registerAsync<RedisClientOptions>({
imports: [ConfigModule],
isGlobal: true,
useFactory: async (config: ConfigService) => {
const store = await redisStore({
socket: {
host: config.get<string>('REDIS_HOST'),
port: config.get<number>('REDIS_PORT'),
},
password: config.get<string>('REDIS_PASSWORD'),
});
return {
store: store,
} as CacheModuleAsyncOptions;
},
inject: [ConfigService],
}),
],
})
export class CacheConfigModule {}What Happens If My App Loses Connection with Redis?
In the unfortunate event of our server losing connection with Redis, our application faces downtime, as evidenced in the following image.
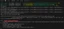
To circumvent this issue, implementing a robust reconnection strategy is imperative. This strategy enables our server to automatically attempt reconnection whenever Redis becomes available.
To enact this solution, we'll configure the reconnectStrategy field. This field dictates the time interval between each reconnection attempt in the event of a connection failure.
In the example below, our application is set to retry the connection every 3 seconds:
useFactory: async (config: ConfigService) => {
const store = await redisStore({
socket: {
host: config.get<string>('REDIS_HOST'),
port: config.get<number>('REDIS_PORT'),
reconnectStrategy: (retries) => {
console.log(`redis reconnect attempt: ${retries}`);
return 3000;
},
},
password: config.get<string>('REDIS_PASSWORD'),
});
return {
store: store,
} as CacheModuleAsyncOptions;
},Nevertheless, if we attempt to shut down the Redis server while our NestJS app server remains active, we encounter an unexpected outcome with our reconnect strategy.
Upon scrutinizing the project logs, a peculiar behavior unfolds: the reconnect strategy attempts to establish a connection once, only to cease all subsequent reconnection efforts. But why?
Handling Redis Disconnection in NestJS
In order to tackle this issue, we first need to understand how NestJS deals with Redis disconnections. We'll need to make a couple of changes to get access to the Redis client and listen for any errors that occur (subscribing to the error event).
useFactory: async (config: ConfigService) => {
const store = await redisStore({
socket: {
host: config.get<string>('REDIS_HOST'),
port: config.get<number>('REDIS_PORT'),
reconnectStrategy: (retries) => {
console.log(`redis reconnect attempt: ${retries}`);
return 3000;
},
},
password: config.get<string>('REDIS_PASSWORD'),
});
return {
store: store,
} as CacheModuleAsyncOptions;
},Upon rerunning the test and disconnecting the Redis service while our app is running, we observe that the error takes the following form:

And if we restart the Redis service, our app won't attempt new reconnections.
What If We Try to Reconnect when the error event takes place?
Thanks to the fact that we are now using the Redis client we can connect and disconnect the service programmatically. This allows to execute a function, that disconnects and reconnects the Redis service. each time the error event is called, as shown in the following example:
const restartRedisService = async () => {
await redisClient.disconnect();
await redisClient.connect();
};
redisClient.on('error', (error) => {
console.log('redis.reconnect.error: ', error);
setTimeout(restartRedisService, 3000);
});In this case, we added the restartRedisService function within a setTimeout to execute the reconnection every 3 seconds. We notice that in the logs, the error shown after the first two reconnection attempts is different; it now includes data such as code and port.
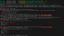
Thanks to error.code, we can now filter and only execute the restartRedisService function if the error code is unknown. When the code is "ECONNREFUSED", our reconnectStrategy starts working.
const restartRedisService = async () => {
await redisClient.disconnect();
await redisClient.connect();
};
redisClient.on('error', (error) => {
console.log('redis.reconnect.error: ', error);
if (!error.code) {
setTimeout(restartRedisService, 3000);
}
});The resulting logs up to this point are shown below:
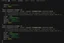
Now that our reconnect strategy works, the last step is to subscribe to the connect and ready events to log when the Redis service is back online.
redisClient.on('connect', () =>
logger.info('redis.connection.connected'),
);
redisClient.on('ready', () => logger.info('redis.connection.ready'));Conclusion
The default strategy in the Redis service configuration is not sufficient on its own. It's necessary to handle errors because, in the case of an unknown error, it's necessary to disconnect and reconnect the client for the reconnectStrategy to work correctly.
This concludes our process of implementing a reconnection strategy in NestJS using Redis.
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ConfigModule, ConfigService } from '@nestjs/config';
import { redisStore } from 'cache-manager-redis-store';
import { CacheModule, CacheModuleAsyncOptions } from '@nestjs/cache-manager';
import {
RedisClientOptions,
RedisClientType,
RedisFunctions,
RedisModules,
RedisScripts,
} from 'redis';
import { CommonModule } from '../common.module';
import { PinoLogger } from '`NestJS`-pino';
const ONE_SECOND = 1000;
@Module({
imports: [
CacheModule.registerAsync<RedisClientOptions>({
imports: [ConfigModule, CommonModule],
isGlobal: true,
useFactory: async (config: ConfigService, logger: PinoLogger) => {
const options: RedisClientOptions<
RedisModules,
RedisFunctions,
RedisScripts
> = {
socket: {
host: config.get<string>('REDIS_HOST'),
port: config.get<number>('REDIS_PORT'),
reconnectStrategy: (retries) => {
logger.warn(`redis.reconnect.attempt.${retries}`);
return ONE_SECOND * 3;
},
},
disableOfflineQueue: true,
password: config.get<string>('REDIS_PASSWORD'),
};
const store = await redisStore(options);
const redisClient: RedisClientType = store.getClient();
const restartRedisService = async () => {
await redisClient.disconnect();
await redisClient.connect();
};
redisClient.on('connect', () =>
logger.info('redis.connection.connected'),
);
redisClient.on('ready', () => logger.info('redis.connection.ready'));
redisClient.on('error', (error) => {
logger.error({ err: error }, 'redis.connection.error');
if (!error.code) {
setTimeout(restartRedisService, ONE_SECOND * 3);
}
});
return {
store: store,
} as CacheModuleAsyncOptions;
},
inject: [ConfigService, PinoLogger],
}),
],
})
export class CacheConfigModule {}







